Get the free the johns hopkins appendix g form serves a critical role for conducting high quality research
Show details
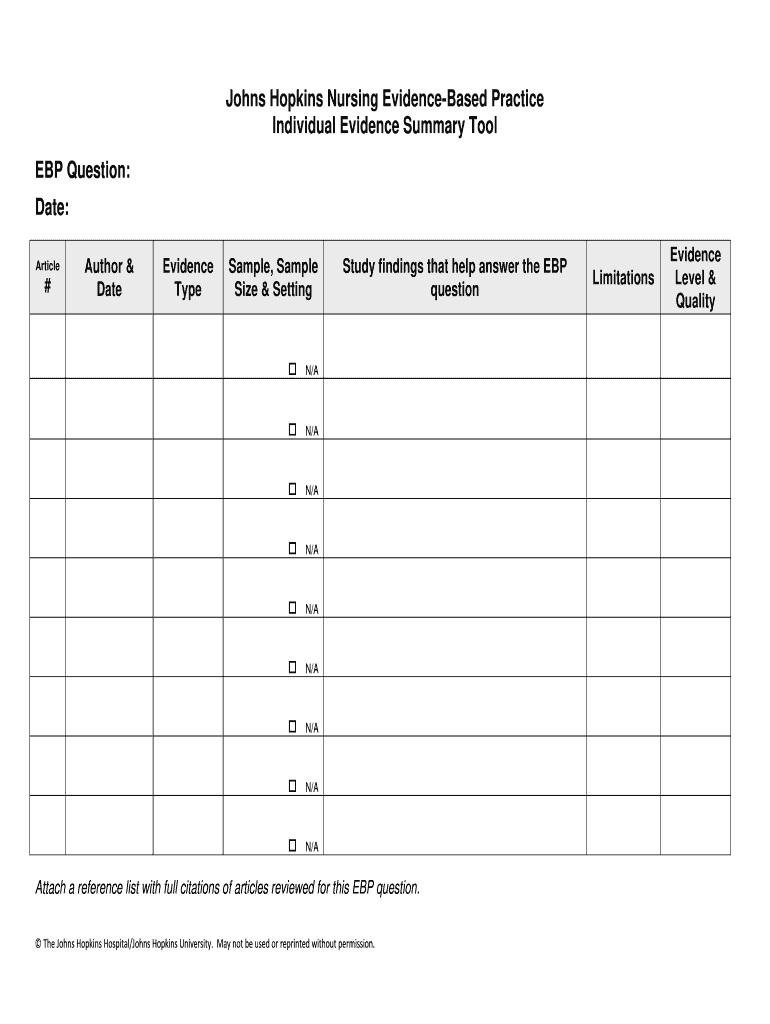
Johns Hopkins Nursing EvidenceBased Practice Individual Evidence Summary Tool EBP Question: Date: Article # Author & Date Evidence Type Sample, Sample Size & Setting N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
We are not affiliated with any brand or entity on this form
Get, Create, Make and Sign johns hopkins individual evidence summary tool form

Edit your johns hopkins evidence appraisal tool example form online
Type text, complete fillable fields, insert images, highlight or blackout data for discretion, add comments, and more.

Add your legally-binding signature
Draw or type your signature, upload a signature image, or capture it with your digital camera.

Share your form instantly
Email, fax, or share your johns hopkins level of evidence form via URL. You can also download, print, or export forms to your preferred cloud storage service.
How to edit john hopkins appraisal tool online
Use the instructions below to start using our professional PDF editor:
1
Set up an account. If you are a new user, click Start Free Trial and establish a profile.
2
Prepare a file. Use the Add New button to start a new project. Then, using your device, upload your file to the system by importing it from internal mail, the cloud, or adding its URL.
3
Edit john hopkins research evidence appraisal tool form. Replace text, adding objects, rearranging pages, and more. Then select the Documents tab to combine, divide, lock or unlock the file.
4
Save your file. Select it in the list of your records. Then, move the cursor to the right toolbar and choose one of the available exporting methods: save it in multiple formats, download it as a PDF, send it by email, or store it in the cloud.
It's easier to work with documents with pdfFiller than you could have believed. You may try it out for yourself by signing up for an account.
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
Your private information is safe with pdfFiller. We employ end-to-end encryption, secure cloud storage, and advanced access control to protect your documents and maintain regulatory compliance.
How to fill out john hopkins ebp model example form

How to fill out john hopkins appendix g:
01
Begin by carefully reading the instructions provided in the appendix. Understand the purpose and requirements of the form.
02
Gather all the necessary information and documents that are needed to complete the form accurately. This may include personal details, medical history, or any other relevant information.
03
Follow the prescribed format or structure of the form. Fill in each section or field with the appropriate information. Ensure that your responses are clear, concise, and relevant to the given prompts.
04
Double-check your entries for any errors or omissions. Review the completed form for accuracy and completeness.
05
Submit the filled-out john hopkins appendix g as per the specified instructions. Make sure to retain a copy for your records.
Who needs john hopkins appendix g:
01
Individuals who are required to provide specific information or undergo certain procedures as part of their affiliation or involvement with John Hopkins University or its related programs may need to fill out john hopkins appendix g. The exact details and circumstances determining the need for this form may vary.
02
Students enrolling in certain courses, programs, or research projects at John Hopkins University may be required to complete appendix g to provide relevant details or consent for specific activities.
03
Employees, faculty members, or researchers associated with John Hopkins University who are involved in specific projects, programs, or administrative tasks might also need to fill out john hopkins appendix g to comply with institutional guidelines or regulations.
Fill
john hopkins level of evidence
: Try Risk Free






People Also Ask about john hopkins appraisal tool appendix e
How do you use an evidence-based practice model?
Although the models include varying levels of detail, they share the following basic phases of the EBP process. Ask: Identify a clinical problem. Attain: Review relevant literature. Appraise: Critically appraise evidence. Apply: Evaluate the need for practice change and potential implementation.
Who created the evidence-based practice model?
Beginning with Florence Nightingale in the 1800s and evolving again within the medical community, evidence-based practice continues to advance along with the nursing discipline.
When was the Johns Hopkins EBP model created?
April 14, 2008 The Institute for Johns Hopkins Nursing, in partnership with Sigma Theta Tau International, the Honor Society of Nursing, has published Johns Hopkins Nursing Evidence-Based Practice Model and Guidelines, a comprehensive book which provides a clear and concise approach to implementing evidence-based
Who developed the Johns Hopkins Nursing Evidence Based Practice Model?
Johns Hopkins Nursing Evidence Based Practice Model Dearholt, S., Dang, Deborah, & Sigma Theta Tau International. (2012).
What is the John Hopkins Appraisal Tool?
Appendix E - Research Evidence Appraisal Tool. The Research Evidence Appraisal Tool helps you decide if the evidence is quantitative or qualitative, and how to use that evidence to support your topic. Appendix F: Non-Research Appraisal Tool. Sometimes you'll find literature that is not primary research.
How do you use Johns Hopkins EBP model?
Evidence-Based Practice is an explicit three step process. Identify the practice question. Identify the best evidence to answer question. Translate the evidence to practice.
Why use Johns Hopkins evidence based practice model?
EBP is a process used to review, analyze, and translate the latest scientific evidence. The goal is to quickly incorporate the best available research, along with clinical experience and patient preference, into clinical practice, so nurses can make informed patient-care decisions (Dang et al., 2022).
When was the Johns Hopkins Nursing Evidence based practice model created?
April 14, 2008 The Institute for Johns Hopkins Nursing, in partnership with Sigma Theta Tau International, the Honor Society of Nursing, has published Johns Hopkins Nursing Evidence-Based Practice Model and Guidelines, a comprehensive book which provides a clear and concise approach to implementing evidence-based
How do you successfully implement EBP?
The 4 keys to implementing evidence-based practices Understand the data. Consider your resources. Establish patient-centered goals. Identify your preferences.
Who created the Johns Hopkins EBP model?
Johns Hopkins Nursing Evidence Based Practice Model Dearholt, S., Dang, Deborah, & Sigma Theta Tau International. (2012).
What is the Rosswurm and Larrabee model?
Rosswurm and Larrabee (1999) The model is based on theoretical and research literature related to evidence‐based practice, research utilization, standardized language, and change theory. In this model, practitioners are guided through the entire process of developing and integrating an evidence‐based practice change.
How do you use the John Hopkins EBP model?
Evidence-Based Practice is an explicit three step process. Identify the practice question. Identify the best evidence to answer question. Translate the evidence to practice.
Who created the Johns Hopkins Evidence based practice model?
The team of Hopkins nursing researchers developed the PET process in 2002, and launched pilot testing the following year with Hopkins Hospital nurses in the PACU (Post-Anesthesia Care Unit) and other areas. In 2004, the model was introduced to a larger Hopkins audience.
Why use the John Hopkins nursing Evidence-Based Practice model?
The Johns Hopkins Evidence-Based Practice model for Nurses and Healthcare Professionals is a powerful problem-solving approach to clinical decision-making and is accompanied by user-friendly tools to guide individuals or groups through the EBP process.
What level of evidence is a cross sectional study Johns Hopkins?
LEVEL 3. Non-Experimental research studies natural occurring phenomena without introducing an intervention. Study designs include exploratory, survey( cross-sectional or longitudinal), and correlational (descriptive, predictive, model testing).
How does the Johns Hopkins EBP model work?
EBP is a process used to review, analyze, and translate the latest scientific evidence. The goal is to quickly incorporate the best available research, along with clinical experience and patient preference, into clinical practice, so nurses can make informed patient-care decisions (Dang et al., 2022).
What is the 6th step in the Johns Hopkins Evidence based practice process?
EBP Practice Question Phase. The practice question phase includes six steps: Step 1: Recruit an Interprofessional Team. Step 2: Define the Problem. Step 3: Develop and Refine your EBP Question. Step 4: Identify the Stakeholders. Step 5: Determine Responsibility for Project Leadership. Step 6: Schedule Team Meetings.
What are the steps of the John Hopkins evidence-based practice model?
It is designed specifically to meet the needs of the practicing nurse and uses a three-step process called PET: practice question, evidence, and translation. The goal of the model is to ensure that the latest research findings and best practices are quickly and appropriately incorporated into patient care.
What is John Hopkins nursing theory?
"The JHNEBP Model is a powerful problem-solving approach to clinical decision-making, and is accompanied by user-friendly tools to guide individual or group use. It is designed specifically to meet the needs of the practicing nurse and uses a three-step process called PET: practice question, evidence, and translation.
Our user reviews speak for themselves
Read more or give pdfFiller a try to experience the benefits for yourself
For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I send jhnebp model to be eSigned by others?
Once your johns hopkins ebp model is ready, you can securely share it with recipients and collect eSignatures in a few clicks with pdfFiller. You can send a PDF by email, text message, fax, USPS mail, or notarize it online - right from your account. Create an account now and try it yourself.
How do I edit johns hopkins evidence based practice model online?
With pdfFiller, the editing process is straightforward. Open your john hopkins research appraisal tool in the editor, which is highly intuitive and easy to use. There, you’ll be able to blackout, redact, type, and erase text, add images, draw arrows and lines, place sticky notes and text boxes, and much more.
How do I edit john hopkins evidence appraisal tool straight from my smartphone?
The pdfFiller apps for iOS and Android smartphones are available in the Apple Store and Google Play Store. You may also get the program at https://edit-pdf-ios-android.pdffiller.com/. Open the web app, sign in, and start editing john hopkins levels of evidence.
What is john hopkins appendix g?
John Hopkins Appendix G is a form used by those affiliated with Johns Hopkins University to provide necessary financial disclosures, typically related to research activities, funding, or other financial interests.
Who is required to file john hopkins appendix g?
Individuals who are involved in research at Johns Hopkins University, including faculty, staff, and sometimes students, are required to file Appendix G.
How to fill out john hopkins appendix g?
To fill out Appendix G, individuals must provide detailed information about their financial interests, potential conflicts of interest, and any external funding sources, following the specific instructions provided by the university.
What is the purpose of john hopkins appendix g?
The purpose of Appendix G is to ensure transparency and manage potential conflicts of interest in research activities at Johns Hopkins University.
What information must be reported on john hopkins appendix g?
Individuals must report any financial interests that could influence their research, including but not limited to consulting fees, stock interests, and other forms of compensation from outside entities.
Fill out your the johns hopkins appendix online with pdfFiller!
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.

Johns Hopkins Level Of Evidence Tool is not the form you're looking for?Search for another form here.
Keywords relevant to johns hopkins research evidence appraisal tool
Related to john hopkins evidence based practice model
If you believe that this page should be taken down, please follow our DMCA take down process
here
.
This form may include fields for payment information. Data entered in these fields is not covered by PCI DSS compliance.